Weldable Aluminum Alloys and Welding Methods
Updated : Dec. 13, 2023Aluminum welding is a manufacturing process that utilizes heat and pressure to join components made of aluminum or aluminum-based alloys. Unlike welded components made of other materials (such as steel), aluminum welding does not exhibit the same level of strength as its base material. Therefore, the selection of the correct base material and welding technique is crucial for achieving the strongest bond between aluminum components.
However, selecting these elements can be challenging, as aluminum welding operations vary significantly based on the product and production specifications, leading to differences in base materials and welding techniques. The following article provides an overview of aluminum welding, enabling customers to better understand which aluminum materials and welding techniques are most suitable for their projects.
Welding performance of aluminum alloy
The 1000 series aluminum alloy, close to pure aluminum, exhibits good weldability. Aluminum in the 1000 series is particularly sensitive to filler type, and 1100 and 4043 are commonly used as fillers. While this type of aluminum has low strength, it demonstrates strong corrosion resistance. It is commonly used in applications involving electrical conductivity or chemical transportation.
The 3000 series aluminum alloy is alloyed with manganese and is easy to weld. Usually, 4043 or 5356 are used as fillers. 3000 is most commonly used in heat exchangers, air conditioning, and similar applications. This alloy series is only of medium strength and therefore has poor performance in structural applications, but is very suitable for bending and forming applications such as bending machines and truck boxes.
Most of the 4000 series aluminum alloys have high weldability, but they are more commonly used as filler materials for other grades. The silicon in these alloys will slow down the cooling rate, solidification rate, and shrinkage stress.
5000 series aluminum alloy is the first choice for weldability. This series uses magnesium alloy, which has very high strength. However, due to the high magnesium content, they should not be welded with 4000 series alloy filler materials. 5000 aluminum is commonly used in structural and heavy-duty applications such as shipbuilding, bridges, and construction.
The welding performance of the 2000 series aluminum alloy is not very outstanding, and it is prone to cracking during the welding process. However, the 2000 series deformed aluminum alloy contains elements such as copper, nickel, titanium, and manganese, with excellent strength. It is still widely used in the aerospace field, but requires specific special welding processes for welding.
The 6000 series aluminum alloy has excellent weldability and strength, and is widely used in welding manufacturing. But the heat affected zone (HAZ) will degrade during the welding process. This will reduce mechanical performance by 30-50%.
7000 series aluminum alloys are similar to 2000 series alloys, but there are not many of them that can be welded because they can crack during welding. However, for example, 7005 is considered weldable because its specific composition does not contain copper. The 7000 series alloy is also widely used in the aerospace field, but the welding process requirements are relatively special.

7 technical difficulties in aluminum alloy welding
1. Oxidation
When welding aluminum, the aluminum oxide layer is an insurmountable difficulty. Its melting point is higher than that of aluminum and requires high heat to melt, but welders must be careful to avoid burning holes on the aluminum surface below.
2. Porosity
Under high-speed heating, the hydrogen absorption rate of aluminum accelerates, and the hydrogen in the molten state is released during metal solidification, forming bubbles, causing aluminum to become porous and fragile.
3. Impurity
Aluminum is very sensitive to pollution and may be contaminated by dirt, air, and water during the welding process. Air pollution can reduce strength and ductility, form oxides that affect appearance, and make multi pass welding complex.
4. Thermal cracking
High levels of thermal stress may lead to thermal cracks in aluminum welds. The combination and treatment of alloying elements can improve the mechanical properties of aluminum alloys.
5. Thermal conductivity
Aluminum has high thermal conductivity, making it difficult for welds to penetrate. Choosing a higher heat input helps to reach the critical temperature for weld penetration.
6. Thickness
Welding aluminum involves materials of different thicknesses, and welders need to know how to avoid burning through thin materials and how to penetrate thick materials to form strong welds.
7. Filler metal
Choosing the best substrate alloy, state, and filling material is crucial. The combination of filling alloy type and post weld process affects the appearance of the weld seam.
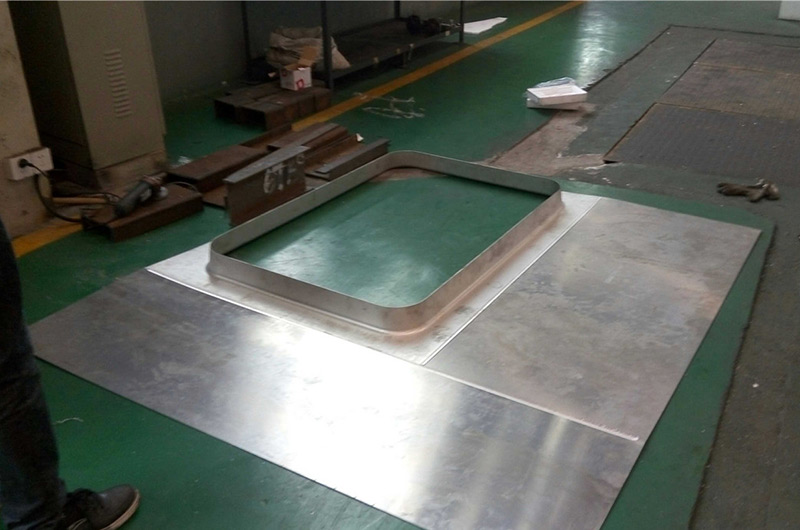

6 tips for welding aluminum materials
1) Thoroughly clean and prepare materials
Proper preparation of aluminum alloy is crucial for effective welding. Pre clean and degrease the metal to remove the outer oxide layer. Fully removing this tough layer will expose aluminum raw materials with much lower melting points. As a reference, the melting temperature of pure aluminum is 1200 ° F, while the melting temperature of the oxide layer is 3700 ° F.
2) Properly storing aluminum materials
Adequate storage of prepared aluminum can prevent re oxidation. As mentioned above, the oxide layer is difficult to remove. You would like to avoid additional preparation and scrubbing.
3) Using a heat sink
A radiator is a supplementary component that absorbs or dissipates unwanted heat. A suitable radiator can ensure optimized heat transfer during welding.
4) Customize your technology for different building materials
As mentioned earlier, the complex chemical structure of aluminum can make welding more complex because it is very sensitive. Before delving deeper, please take time to conduct research, evaluate your materials, and refine your skills.
5) Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment
We are once again committed to educating and protecting our customers. Therefore, we urge all manufacturers to wear necessary personal protective equipment (PPE) when processing or using any metal. For example, when welding aluminum, we strongly recommend wearing a respirator!
6) Be patient and not in a hurry
Completing the welding process at high speed is undoubtedly dangerous. No matter how much personal protective equipment you wear, the best protection is practical knowledge!

What aluminum alloy welding methods can Chalco provide?
- Tungsten inert gas arc welding/argon arc welding
- Melting electrode gas shielded welding
- Laser beam welding and electron beam welding
- Resistance welding
- Welding rod - shielded metal arc welding
- Flux cored wire arc welding
- Gas shielded metal arc welding
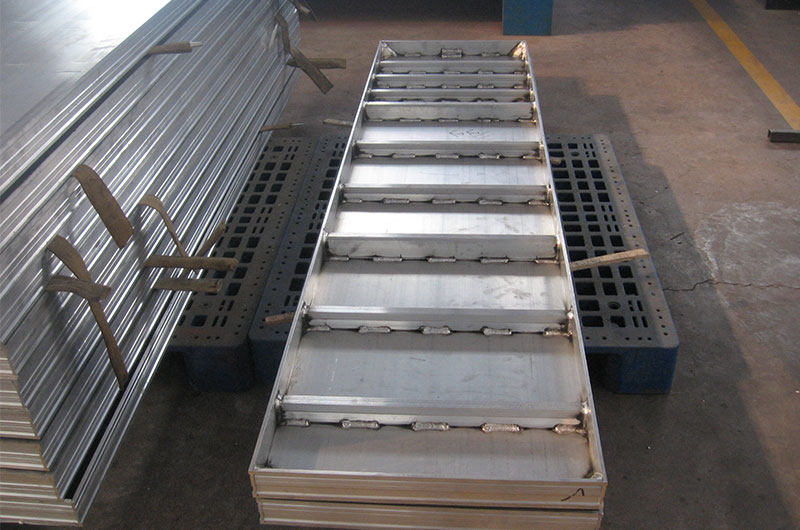

Chalco's hot selling solderable alloy products and application fields
Chalco, as a professional aluminum plate manufacturer and supplier, can provide customers with value-added welding services for aluminum plate purchases. We have extensive experience in the aluminum plate production and processing industry. Through professional knowledge reserves and service skills, making your aluminum plate purchase easier and more convenient, the aluminum plate project can be solved as a whole in one go.
| Alloy | Advantage | Disadvantage | Common applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3003 | A very popular universal alloy. | Excellent formability and weldability are not particularly strong. | Sheet metal processing, stamping, fuel tanks, cookware, electronic products. |
| 5052 | Stronger than 3003. | Good weldability and excellent corrosion resistance. | Pressure vessels, storage tanks, hydraulic pipes, electrical appliances, and ship applications. |
| 5083 | High welding efficiency and very high joint strength. | Not heat treatable. | Drilling rigs, storage tanks and ship components, low-temperature applications. |
| 5454 | Medium to high strength, excellent weldability. | Not recommended for cladding. | High heat applications, such as truck transportation using hot asphalt road tankers and dump trucks, as well as some chemical storage containers, such as hydrogen peroxide. |
| 6061 | A good all-around alloy. | - | Structural and welded components, train carriages, pipelines, aircraft, automotive components. |